Friday, 27 November 2020
5 Metastatic Liver Lesions of a GIST
5 Metastatic Liver Lesions of a GIST
2:05
Tissue sparing approach for five metastatic liver lesions of a Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST). All successfully treated in one continueous session. Quality Ablation was preferred over surgical resection to facilitate a speedy recovery after the intervention, offer the patient a better quality of life and preserve options for future treatment, since the patient is likely to develop more metastatic lesions over time.
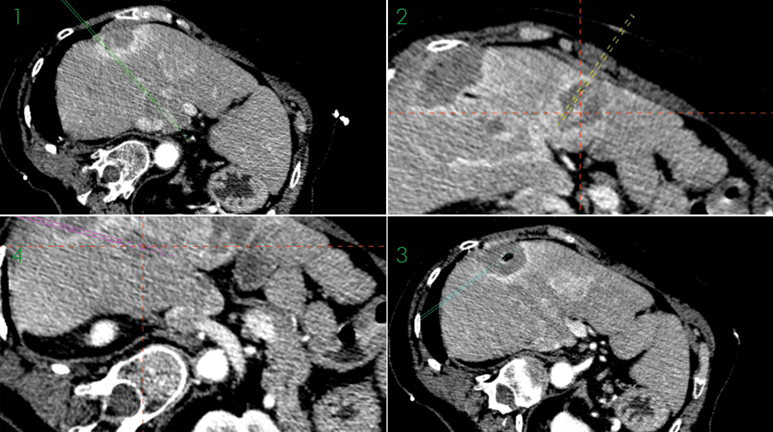
1. Ablation Validation after treatment of lesion in Seg I
2. Ablation Validation of lesion close to gallblader
3. Ablation Validation of lesion in liver dome
4. Ablation Validation of lesion in Seg V
2. Ablation Validation of lesion close to gallblader
3. Ablation Validation of lesion in liver dome
4. Ablation Validation of lesion in Seg V
Name: Prof. Dr. Thiery Chapelle & Dr. Bart Op de Beeck
Institution: Antwerp University Hospital, Antwerp, Belgium
Patient age and sex: 76 years, female
Initial condition:
- 2014, small intestine perforation with characteristics that fit a Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
- Diagnosis Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST), T2Nx was confirmed through biopsy
- After surgery start adjuvant glivec for three years
- Small intestine was resected after discovery of GIST
- Patient has arterial hypertension
- 2020, five metastatic liver lesions from the GIST
Planingvideo of the needle trajectories
Treatment:
- Treatment strategy: Quality Ablation or major surgical resection
- Decision for minimally invasive intervention to preserve parenchyma for future treatment options, because patient is likely to develop more metastatic lesions over time
- Resection in this case would mean removing several sections of the liver, which would affect the function of the liver and also result in a long hospitalization and recovery.
Result:
- With Quality Ablation the most tissue sparing approach was chosen, to facilitate a speedy recovery, offer the patient a better quality of life and preserve options for future treatment, since the patient is likely to develop more metastatic lesions over time


